VANTA Network
Creates a decentralized and safe blockchain layer for network and real-time communication.

BOASTS is a decentralized and unlicensed network that ensures real-time, safe and personal connectivity. By using blockchain and crypto-economics designed for real-time networks, VANTA creates a system where nodes participating in the network contribute to the transmission and processing of real-time data without relying on traditional systems and networks that are centralized. This system produces a low-cost blockchain-based functional network where anyone, regardless of the existing platform, can participate and use the network using the API, SDK, or modules to be integrated with existing applications or platforms that are used. In simpler terms, creative services will be provided and integrated in the VANTA ecosystem,
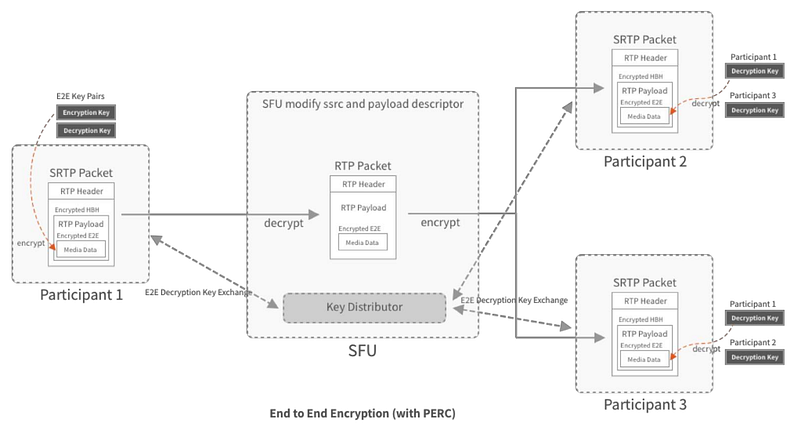
Intelligent Network VANTA functions as a decentralized network that transmits data, processing, and storage functions in real time by selecting partners who collaborate and evaluate each other. The VANTA Ecosystem also includes a Network Framework which is a non blockchain framework that builds on PGP encryption standards that help networks achieve high levels of performance when dealing with secure real-time communication and data transfer. Furthermore, the ARKAS Protocol, a decentralized P2P network protocol, establishes a smooth routing channel across all nodes,
The team behind the project stated that VANTA is a decentralized and unlicensed network that ensures real-time, safe and personal connectivity, and they imagine that their network technology will cover a variety of use cases. These include messaging, file transfer, development of voice and video calls, large-scale real-time video streaming, and transmission and processing of real-time data collected from IoT sensors. In addition, VANTA will also provide and expand enterprise-level telecommunications network solutions for business and customer companies.
PURPOSE / OBJECTIVE
Benefits
Develop and operate real-time communication services that are measurable, reliable and very safe at low cost.
Use a variety of high-quality services free or almost free without worrying about privacy.
Building a blockchain-based telecommunications network between various organizations.
Problems and solutions
VANTA will try to solve the following problems:
1. Increase network bandwidth and costs.
Current networks and infrastructure that support various networks in real-time reach bandwidth limits. VANTA solves the problem of bandwidth and costs by providing computers and ordinary mobile devices throughout the world, whose performance is increasing rapidly every year, and will help create networks in real time.
2. The cost of developing real-time networks and problems with centralized services.
Many companies are limited or cannot develop real-time network services. Many companies are forced to use centralized API services, which require increased costs, providers can stop API services without notice and data stored on centralized servers does not guarantee their security and confidentiality. This problem was solved by making decentralized networks for real-time networks, which did not belong to anyone and were not controlled by anyone.
3. Confidentiality issues arising from the transfer and storage of personal data.
Data that will be sent and stored on a centralized server can be stolen. Using the blockchain, the process of transferring, storing and deleting data will be independent and transparent. And decentralized nodes transmit and store data in real-time mode preventing data from being stolen or misused.
4. Access to data generated by the device, and costs for using data.
VANTA intends to create an efficient system that can quickly and safely send and receive data in real time, creating a competitive system that instantly configures the network according to each situation.
5. Confidence in communication between parties and trust in data sent from various devices.
In the near future, there will be more contact between people and devices in real time, this will require reliable estimates. Trust will be achieved in the future, regardless of whether the person is involved in daily life or the company does business.
VANTA network
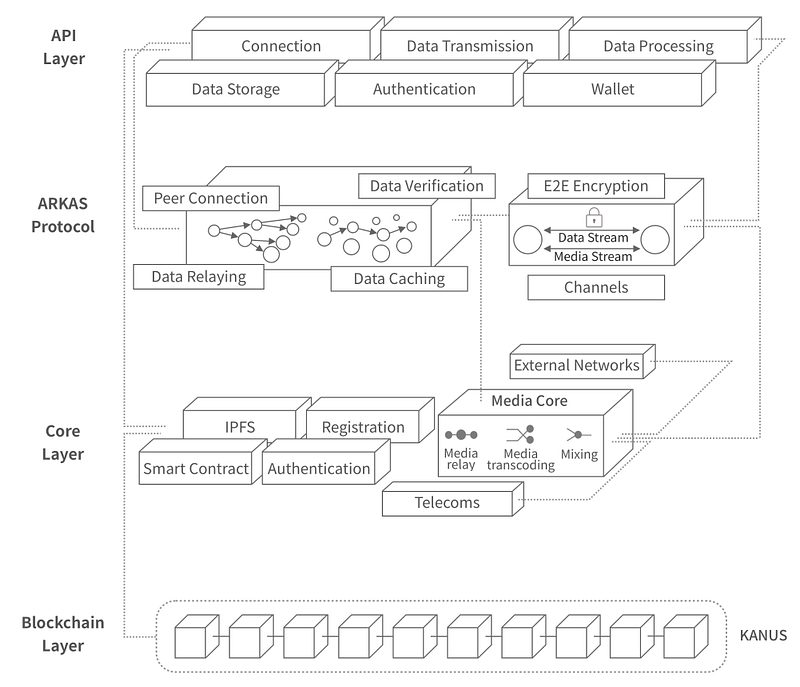
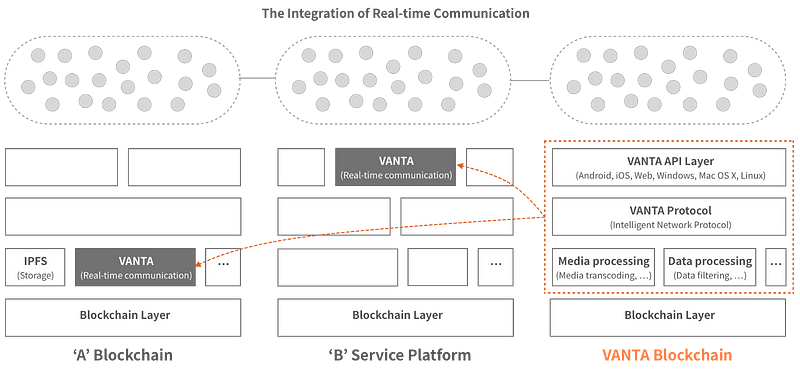
VANTA Network Infrastructure consists of four main layers.
1 – Blockchain Layer (CANUS)
The VANTA network combines Proof of Networking (PoN) with Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) and Verifiedable Random Functions (VRF) to form a pre-ordered PoN-VRBFT consensus algorithm. Pretty mouthful right? Previous BFT and VRF have been used in combination on projects such as Algorand and Ontology , but these projects combine Proof of Stake (PoS) with BFT and VRF, while VANTA Networks use PoN in combination with both methods.
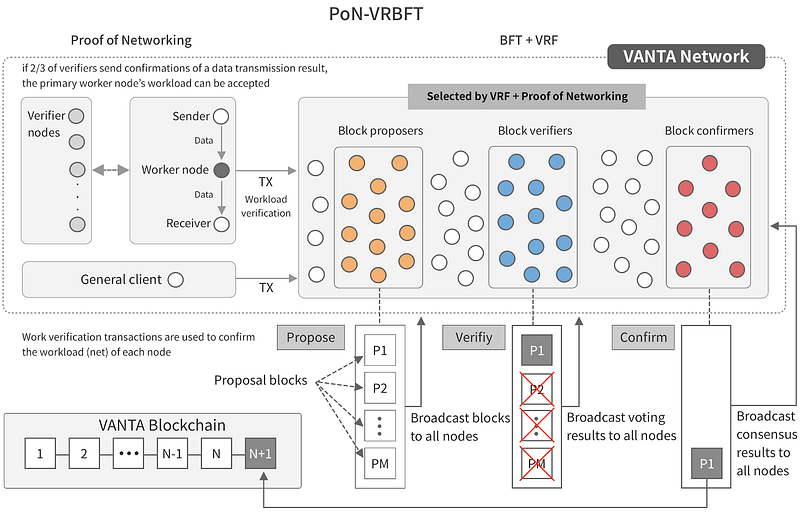
- Proof of Networking (PoN)
Proof of Networking is an algorithm that mandates each node that has competitively contributed for direct data communication, processing and storage to prove their workload and use that evidence data when participating in a consensus round. The workload of each node is verified by the verification node selected through VRF, and is recorded using VANTA’s unique workload unit called net and net prices to prove the amount of workload and its actual value
. This is what distinguishes Proof of Networking from other consensus algorithms.
. This is what distinguishes Proof of Networking from other consensus algorithms.
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
In P2P networks, consensus is achieved if nodes that are loyal, or not wrong, reach unanimous agreement on their decisions. Byzantine Error Tolerance means the incoming message is repeated to another recipient of the incoming message. All nodes make the assumption that the message repetition action overrides the Byzantine node problem.
- Verifiable Random Function (VRF)
Verifiedable Random Function (VRF) is a pseudo-random function that provides evidence that can be used to verify the authenticity of its output publicly. This is widely used in the VANTA real-time network competition model and blockchain consensus algorithm. By using VRF, VANTA Network can reduce the time nodes have to communicate with each other to reach consensus, allowing blocks to be generated at a much faster speed.
Basically this consensus algorithm has been developed, and is needed because of the real-time nature of the data passed on the network. Combining these three concepts increases the security, scalability, and transaction speed of the existing consensus algorithm, which allows VANTA Network to process data at the speed required for sending “real-time” data.
The VANTA network is supported by a series of P2P nodes. Users can download the VANTA core client on a computer or mobile device, install a VNT token and participate in the VANTA Network by processing workloads. Certain applications released on the VANTA Network will also give users the ability to actively participate in the network. The selected node and processing workloads qualify for some block prizes, based on their contribution to the workload itself (the specifics are discussed in more detail in the Utilities Token section below).
At present there are no guidelines for how many VNT tokens are needed at stake at each node level, or hardware requirements to run each type of node.
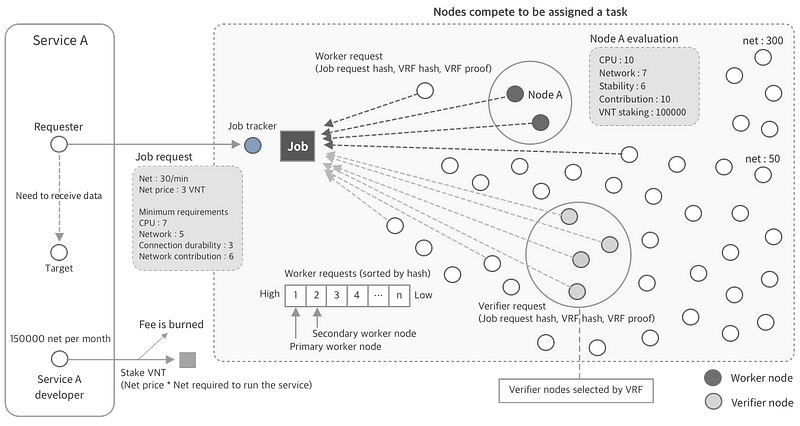
- Job Tracking Node
The first node that receives a job request from the requesting node becomes a job tracker. The job tracker is only valid for job requests. The job tracker is responsible for verifying and broadcasting job requests, managing selected nodes to process jobs, connecting existing workers and applicants and more. Job trackers also send job transactions.
- Primary Worker Node
This is the node that is carrying out the actual task immediately after processing the job begins.
- Secondary Worker Node
This is a node that waits until the end of work processing, and when the primary worker node experiences performance problems during processing or network problems occur, it takes over the task immediately.
- Node Verifier
Node Verifer verifies if the worker node has been correctly selected and the worker node has performed the task correctly. Next, the node issues proof of the work node of the worker to the worker node.
The Verifer node requires a smaller number of VNT tokens, and because of reduced workload, it can be run at a far lower device than the worker node.
2 – Core Layer
The core module of the ARKAS protocol, implementation of the main functions performed by colleagues in the network.
3 – Protocol Layer (ARKAS)
Protocol that allows partners to build intelligent VANTA networks. The ARKAS protocol allows colleagues to transmit data, processing, and real-time storage by selecting and evaluating colleagues. This is a growing network that strengthens the scalability, reliability, efficiency and privacy of real-time networks by creating competitive systems based on resources such as computing power, network bandwidth, and reliability.
4 – API layer
The API layer is a layer where companies or users can connect external services / applications to the VANTA Network by using the VANTA API and SDK.
API users are required to install VNT tokens to use the API, which allows full access to network services, such as data transfer, processing and storage in and across the VANTA Network. In addition, API users are required to store VNT tokens to use network resources (known as workloads). When canceling a token 2% of the token at stake will be charged as a fee and the token will be burned.
TOKEN SALE: SINCE 14 JAN at https://www.cashierest.com
ROADMAP
According to the roadmap, testnet VANTA is planned to be released in Q2 2019 and mainnet is scheduled for Q3 2019.
VANTA plans to conduct an Initial Exchange Offering (IEO) and not a common Initial Coin Offering (ICO).
The current IEO date is TBA.
Team
The core team of the VANTA Network consists of 26 members, many of whom have worked for Voiceloco . A complete list of all team members can be found on the VANTA Network website - https://vanta.network/TeamFull

Wolf Crypto Resources
Website: https://vanta.network
Twitter: https://twitter.com/vantanetwork
Telegram: https://t.me/vantanetwork
Bitcointalk: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=5095100
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/vantanetwork/
Username: Schildhauer
Link: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2354217
Link: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2354217


Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar